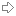
封裝class Student2{
private String name; //
private int age; // 3~30
private float score;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public float getScore() {
return score;
}
public void setScore(float score) {
this.score = score;
}
}
多態(tài)
abstract class Animal{
// 抽象方法:只有聲明,沒有實現(xiàn)(花括號里面那部分)
public abstract void run();
// 普通方法:聲明+實現(xiàn)
public void eat(){
System.out.println("Animal is eating...");
}
}
繼承
class Dog extends Pet{
private String color;
public Dog(String name, int age, int health) {
// super 超類��、父類��,調(diào)用父類的構(gòu)造方法
super(name, age, health);
}
public Dog(String name, int age, int health, String color) {
super(name, age, health);
this.color = color;
}
public String getColor() {
return color;
}
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Dog{" +
"color='" + color + '\'' +
"} " + super.toString();
}
}
抽象類 abstract
abstract class Animal{
// 抽象方法:只有聲明���,沒有實現(xiàn)(花括號里面那部分)
public abstract void run();
// 普通方法:聲明+實現(xiàn)
public void eat(){
System.out.println("Animal is eating...");
}
}
接口 interface
interface Fly{
// public abstract 可以省略
public abstract void fly();
}
// 實現(xiàn)類
class Bird implements Fly{
@Override
public void fly() {
System.out.println("鳥在樹林中飛。");
}
}
class Plane implements Fly{
@Override
public void fly() {
System.out.println("飛機在空中飛��。");
}
}
關(guān)鍵字 final
final class A {}
//class B extends A {} // 類A不能被繼承
class B {
final float PI = 3.14F; // 常量
public static final float pi = 3.14f; // 常量
public final void func(){
final String name;
name = "Hello";
// name = "Hello world"; // 只能被賦值一次
// PI = 3.1415926F;
}
}
靜態(tài) static
public static void getCount(){
// 非靜態(tài)的成員變量��,在靜態(tài)方法中不能使用
System.out.println(/*name + */"當前票數(shù):" + count);
}
|
 客服電話
客服電話

 官方微信
官方微信